Anjing Road, Xiaolan, Zhongshan, Guangdong, China
info@mes-drive.com
08.00 AM-09.00 PM
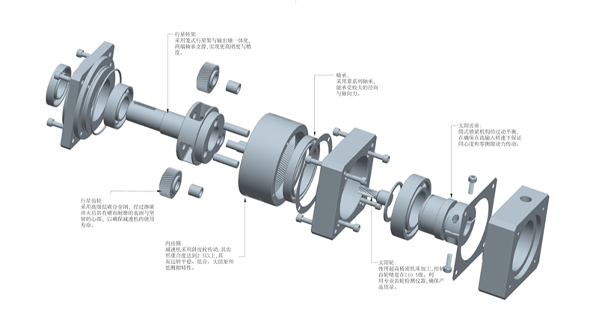
Complete knowledge of gear reducer transmission
Gear transmission is a mechanical transmission that utilizes the meshing of teeth between two gears to transmit power and motion. Among all mechanical transmissions, gear transmission is widely used to transmit motion and power between two shafts that are not far apart in relative position.
Characteristics of gear transmission:
High efficiency, in commonly used mechanical transmissions, gear transmission has the highest efficiency, and closed transmission has an efficiency of 96%~99%, which has great economic significance for high-power transmission;
Compact structure, requiring less space than belt and chain drives;
Stable transmission ratio is often a fundamental requirement for transmission performance. Gear transmission has been widely used precisely because of its characteristic;

A gear transmission that is reliable in operation, has a long lifespan, is designed and manufactured correctly and reasonably, and is well maintained. It is highly reliable in operation and can last for up to ten to twenty years, which is unmatched by other mechanical transmissions. This is particularly important for vehicles and machines working in mines;
However, the manufacturing and installation accuracy requirements for gear transmission are high, the price is expensive, and it is not suitable for situations where the transmission distance is too large.
Types of gears
1) Gears can be divided into involute gears, cycloidal gears, circular arc gears, etc. according to their tooth profile. Involute gears are easy to manufacture and widely used, while cycloidal gears and circular arc gears are less commonly used.
2) Gears are divided into cylindrical gears, bevel gears, racks, and worm gear transmissions according to their appearance.
Dimensions of spur cylindrical gears
(1) Names and geometric dimensions of each part of spur cylindrical gears
(2) Main parameters of spur cylindrical gears
1) Number of teeth z. The total number of teeth on a gear, denoted as z. When the modulus is constant, the more teeth there are, the larger the geometric dimensions of the gear.
2) Modulus m. The quotient of the tooth pitch p and the circumference π is called modulus, represented by m, i.e. m=p/m, in millimeters. The modulus wheel is the basic parameter of gears. When the number of teeth is equal, the larger the modulus, the larger the size of the gear, and the stronger the load-bearing capacity. Gears with equal pitch circle diameters have a higher modulus and stronger load-bearing capacity.
Comments (2)
Rasel ArnoldJan 24, 2024
Though author order shouldn't matter, industry custom and practical limitations say otherwise.
Ryans JosephJan 22, 2024
Though author order shouldn't matter, industry custom and practical limitations say otherwise.